Status of the Battery Industry
Korea is a global leader in the battery industry aiming to turning crisis to opportunity amidst changes in the global trade environment
The battery industry is playing a key role in the global energy transition and is growing rapidly based on carbon neutral targets set by developed countries to respond to climate change and the electrification of vehicles. In particular, electric vehicles (EVs) emerged as a solution to carbon neutrality and circular economy, and are driving the growth of the battery industry. With interest rate increases slowing down the global economy and the war in Ukraine pushing up energy prices in Europe, there are concerns over the slowdown of the EV market, but these are short-term setbacks caused by external factors and the battery industry is expected to continue growing steadily in the mid- to long-term. The growth rate forecast for the EV market has been revised downward as it enters the chasm, but plans to ultimately ban the sale of internal combustion engine vehicles in major countries is still effective, and OEMs are expected to invest more in EV production in stages to meet the steadily growing demands for EVs
Table 1. Deadlines for Sales of International Combustion Engines
* US carmakers are required to produce two thirds of its new cars as EVs and hydrogen cars from 2032.
Korea is leading the global battery industry in small batteries for laptops and cell phones, and is also in a leading position in rapidly-growing markets of medium and large secondary batteries, such as EV batteries and energy storage systems (ESS). Currently, Korea holds a 37% market share of the global battery market and is second only to China in terms of volume. At the same time, the country enjoys the biggest share or 54.1% in markets excluding China.
Table 2. Market Share in Global Markets Excluding China
* Source: SNE Research
Despite the strong growth of Korean battery makers, the recent global trade environment is anything but favorable. The reorganization of global supply chain in blocks and the spread of resource nationalism pose significant burdens for Korea as it is highly dependent on overseas materials and minerals. Major developed economies such as the US and the EU are striving to foster the battery industry at the national level as it is crucial in achieving carbon neutrality and energy transition. They are also introducing policies to support the battery industry on a large scale, such as the IRA in the US and the CRMA in Europe, and to internalize the supply chain of key minerals and materials. As a result, they are pulling in overseas investments like a black hole and are rapidly building a battery industry base in their countries. Korean battery makers are estimated to have won orders worth KRW 1,000 trillion, and the nation’s three major battery makers are planning to invest KRW 52 trillion by 2025, mainly in the US and EU. In addition, battery material companies are increasing their investments in countries with rich resources such as Canada, Australia, and Indonesia, and are also making investments to grasp opportunities in the future battery recycling market.
Market Outlook and Government Policies to Foster the Battery Industry
With the EV market slowing down, Korea is faced with challenges to diversify portfolio, build smart factories and establish supply chain
Global EV sales are expected to grow at a CAGR of over 19% from 6.7 million units in 2021 to 78.8 million units in 2035. The EV battery market is expected to grow from 449 GWh in 2021 to 5,853 GWh by 2035, at a CAGR of 20%.
Figure 1. Global Battery Market: Current Status and Outlook
(Unit: GWh)
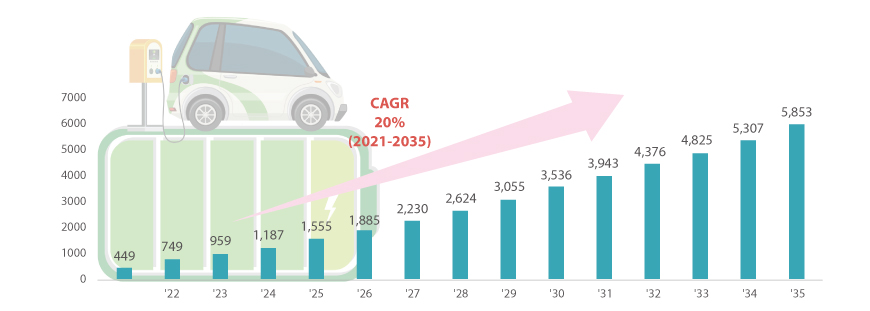
- 2021년 449GWh
- 2022년 749GWh
- 2023년 959GWh
- 2024년 1187GWh
- 2025년 1555GWh
- 2026년 1885GWh
- 2027년 2230GWh
- 2028년 2624GWh
- 2029년 3055GWh
- 2030년 3536GWh
- 2031년 3943GWh
- 2032년 4376GWh
- 2033년 4825GWh
- 2034년 5307GWh
- 2035년 5853GWh
- CAGR 20%(2021년~2035)
* Source: SNE Research
Going forward, the EV battery market is expected to be divided into the entry-level LFP and premium NCM markets, and competition in the mid-market is expected to intensify. In order to capture the volume market, the three major battery makers are diversifying their material portfolio to include LFP, mid-nickel, and manganese-rich batteries in addition to their current focus on high-nickel batteries. They are also making efforts to diversify form factors to include cylindrical, square, and pouch. This year, the Korean government approved a technology development project worth KRW 110 billion to develop next-generation batteries (lithium-sulfur, lithium metal, solid-state, etc.). Battery makers are also closely watching developments in the automation of the battery manufacturing process. They are also expanding production bases by investing overseas and building smart factories to ensure high cost competitiveness and yield. These efforts are expected to clear problems such as high labor costs and yield variance in North America and Europe. Stable supply chain is another important factor in producing batteries as Korea makers import a high proportion of materials. The introduction of legislations on supply chain such as the IRA in the US and CRMA in Europe highlighted the importance of securing a stable and sustainable supply chain in the EV and battery industry. The government is providing comprehensive support for the internalization of the battery supply chain by enacting and revising the Act On Special Measures To Strengthen Competitiveness And Stabilize Supply Chain Of Materials, Components, And Equipment Industry to closely manage items that are highly dependent on certain countries and granting benefits to companies that contribute to supply chain stabilization.
Overseas Battery Makers Investing in Korea
As a result of the government and companies continuously making efforts to attract investment since the US government’s announcement of the IRA, the processing of cathode material components was accepted as a mineral processing process in the proposed guidance for the electric vehicle tax credit, making it easier for battery makers to meet the IRA parts and minerals requirement if the precursors of cathode material components are processed in Korea, a free trade partner of the US.
As a result, Chinese companies are increasing their presence in Korea by forming joint ventures with Korean companies as a means to fulfill the IRA requirements. Major materials companies such as EcoPro, LG Chem, and POSCO Future M have announced joint ventures with Chinese companies such as Zhejiang Huayou Cobalt and CNGR to produce precursors, and are investing in industrial complexes in Saemangeum and Pohang that have been designed by the government last year to specialize in batteries.
Table 3. Overseas Battery Makers Investing in Korea
By Joonsoo Kim (jskim@k-bia.or.kr)
Manager, Policy Support Team, Korea Battery Industry Association (KBIA)













