Industry Trends
- Home
- Jeju Life
- Industry Trends

Kim Ki-Hong, explaining the Jeju smart city project at the Drone Integrated Control Center
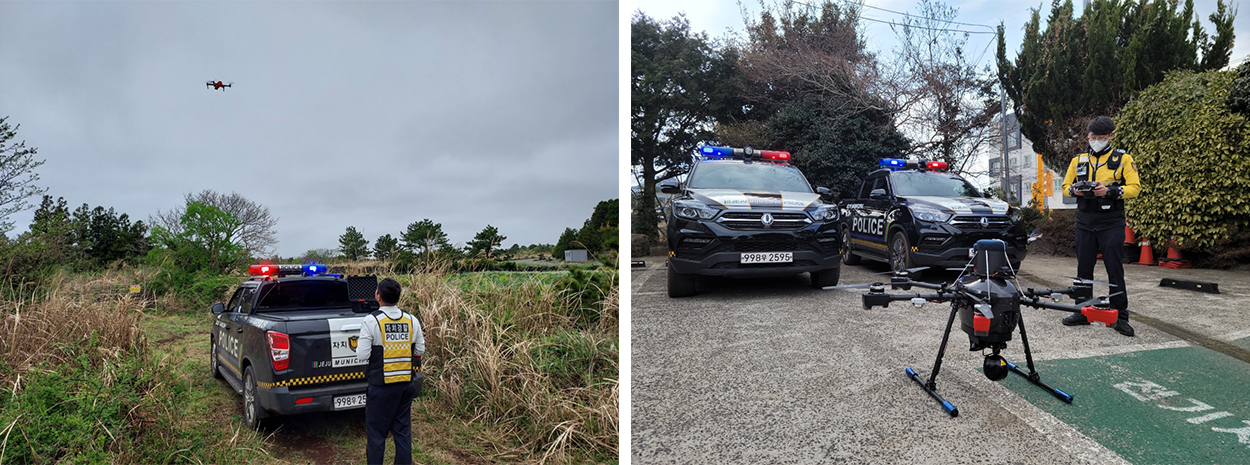
How can we find out that trees in a forest are dying suddenly? How can we figure out when there is a problem with complex gas pipes installed in a city? Is there a way to ask for help when someone is injured while climbing Hallasan Mountain? The answer is drone. Drone technology built on Jeju-style IoT is used to eliminate trees afflicted by infectious diseases, monitor gas pipes in the city in real-time, and send rescue items to people trapped in Hallasan.
Jeju-style IoT also enables us to track the movement of vehicles for special schools, transfer emergency patients rapidly based on collaboration between a fire station and a hospital, and treat patients by checking the sickbed availability of hospitals at once.
The challenge is about addressing accidents that occur continuously throughout the day with future technology. Today, we met Kim Ki-Hong from the Future Strategy Bureau Digital Convergence Division of the Jeju Special Self-Governing government. He is driving the smart city challenge project, a plan to build a new form of urban ecosystem for the future generation.

JEJU is driving the smart city challenge project.
Future Technology's Power to Keep Jeju Clean
The Jeju Special Self-Governing government is busy with its smart city-building project. The project team's priority is to build Jeju-style IoT, the foundation of all other projects. At the same time, the team works on futuristic projects relevant to innovative growth, such as aerospace, private rockets, UAM (Urban Air Mobility), and drones.
"70% or more of the industry in Jeju Special Self-Governing Province is driven by agriculture, tourism, and construction. For the island to do business with future innovative growth technology, it needs to change its industrial structure. Urban development projects operated with a vast budget are not the way forward if Jeju is to protect its environment and change its industrial structure. Jeju needs to develop its unique strategy in building a smart city as it takes the environment into consideration throughout its development." The statement clearly shows why Jeju tries to address regional issues through digital technology and data.

Jeju is working on a smart safety system that finds missing people with drones and monitors illegal activities.
The Jeju-style smart city is about providing digital public services to address current issues in Jeju, including transportation and the environment. The project aims to give a sense of convenience to residents and tourists, build the foundation for companies to grow, change Jeju's tech industry landscape, and ultimately form a software-based futuristic city.
The parts operated in analog forms must be converted to digital formats and saved in a database for digital conversion to happen. Jeju Big Data Center and Jeju Data Hub will receive the real-time information generated through IoT devices in Jeju. "Data gets accumulated and regenerated in a platform, creating a new business. Without data, there is no technology like AI or blockchain."
In addition, once the Korea Satellite Operation System is built as Jeju plans, data can be collected, analyzed, and developed with satellites. Jeju is considering establishing the Satellite Information BigData Center with the Ministry of Science and ICT and the Korea Aerospace Research Institute. "Jeju, an electric wave-free area and data generator, is the optimal place to build the Korea Satellite Operation System. For Jeju to grow based on future technology, such as private rockets, local government level support and policy should be ready."”
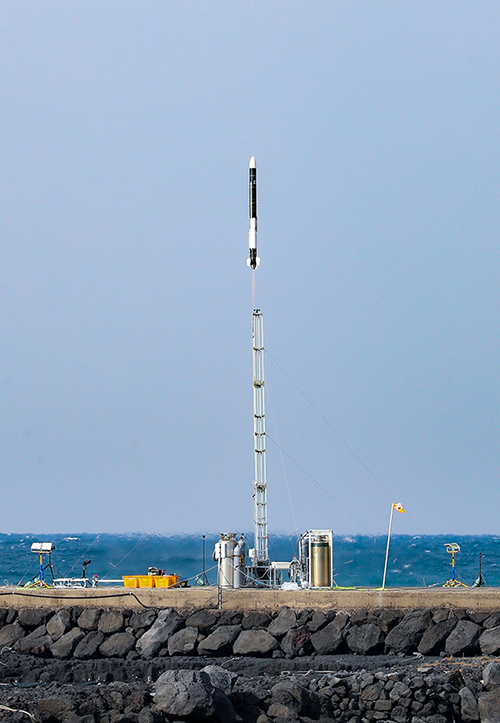

On 29 Dec 2021, a private rocket launch was made successful for the first time in Korea.
The Public Sector Builds, and the Private Sector Realizes
Jeju considers private-public collaboration as the most critical factor in materializing future tech. "Mediating systemic issues that arise from developing advanced technology with the central government and collaborating with companies are the most important roles Jeju can play," says Kim Ki-Hong. He believes that "A smart city can be built as long as public policy and systemic intention to push the project are aligned. Also, collaboration with the private sector is a must if one intends to realize and actualize the project and connect with future industries." From the mid-to-long-term perspective, Jeju continues to change the system while working with the central government. One of Jeju's efforts is shown by the case where Jeju was approved as the largest Drone Special Freedom Zone in Korea after negotiating countless times with the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, and Transport.
"There is currently no nation-level system to support satellite and space projects. Thus, local governments need to help private entities engage in projects and grow through systemic support, like postponing the entry into the application of regulations. In other words, Jeju should help the private sector create results by enacting a special act on future techs, such as the UAM special act."
Jeju's commitment to supporting new industries is well reflected in progress made in diverse sectors, including satellite, private rockets, and UAM. On 29 Dec 2021, a private rocket launch was made successful for the first time in Korea. "Unlike the national project Naro, Perigee Aerospace had difficulty finding a place to advance its tech and infrastructure as a private startup. Jeju actively collaborated with the central government, persuaded residents, and became the first province in Korea to fire a private rocket built by a startup as a public entity. Likewise, the industry that uses future tech can progress when the public sector collaborates with the private sector."
An ultra-precision bus locating service provided by Kakao
Taking Care of Daily Life and Advancing to the Future
Kim Ki-Hong believes that "Smart city projects have to be connected with public services so that residents and tourists can feel them in their daily lives." One of the services that shows this spirit is the Kakao ultra-precision locating service, which boasts a high usage rate among residents and tourists.
The service tracks location data of city buses owned by Jeju on a real-time basis and shows the data on an application developed by a private company. The service, Kakao Ultra-precision Bus Location Service, is a representative public-private cooperative project. The project improved the quality of the service and introduced a new form of tourism in Jeju by changing it from a car rental-focused tour to one that links buses and walking tours.
"Services provided by the public sector are often not easily accessible for residents. Thus, it is important to adopt the viewpoint and approach of the private sector in making service easier to access if one is to increase service usage of residents and tourists."
Recently, Jeju has been leading efforts in advancing the IoT service that shows the detailed location of clean houses near the residential area, the collection point for disposable cups, and public toilets. Jeju Wheel Navi, a navigation system for people in wheelchairs developed for the mobility handicapped, was born from a project selected through a platform that collects proposed ideas of its citizens. Wheel Navi road, which realized the interior spatial map with digital twin tech, provides voice information on downhills, stairs, angle of the slopes, and accessible toilets. The case showed the possibility of underlying tech.
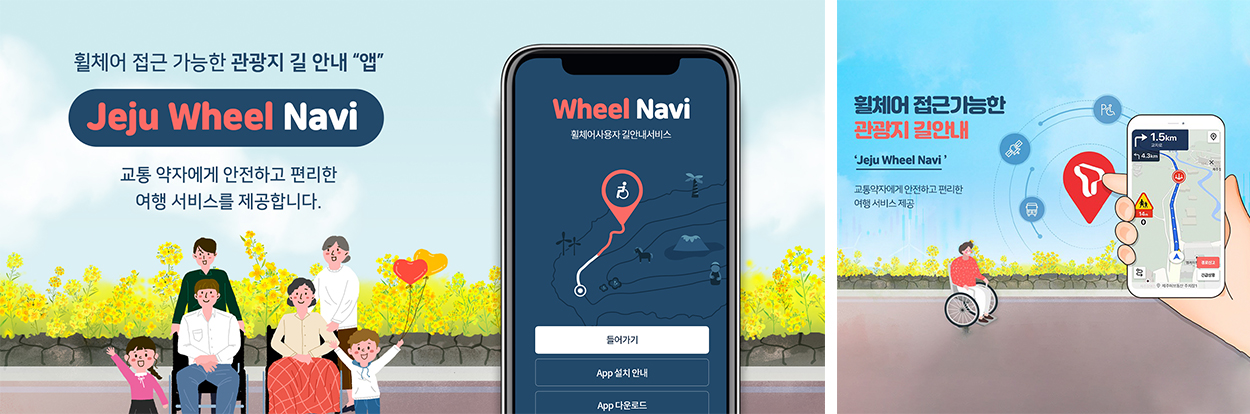
Jeju Wheel Navi, a navigation service for the mobility handicapped on wheelchairs
Jeju is drawing a future where an ultra-precision bus becomes a huge IoT platform and lets people in the margin use the service through digital tech. It is nurturing dreams in Jeju and building a future. Jeju smart city project's goal is to make Jeju's tech become resources for the private sector and eventually change the industrial structure of Jeju through the infrastructure built with its tech.
