Energy storage, or ESS, is the capture of energy produced at
one time for use at a later time. It consists of energy storage,
such as traditional lead acid batteries and lithium ion batteries,
and controlling parts, such as the energy management system
(EMS) and power conversion system (PCS). Installation of the
world’s ESS has increased from 700 MWh in 2014 to 1,629
MWh in 2016. Battery-type ESS is being actively adopted,
especially lithium ion batteries, due to its great potential for
growth. This is largely due to its transformation efficiency and
environmental friendly traits. Experts forecast the global lithium
ion battery market to expand from 1.8 GWh in 2016 to 8.5 GWh
in 2020 and 16.2 GWh in 2024. The global ESS market in 2016
was about USD 2.56 billion. This amount is expected to
increase to USD 15 billion in 2020 and USD 29.2 billion in
2025.
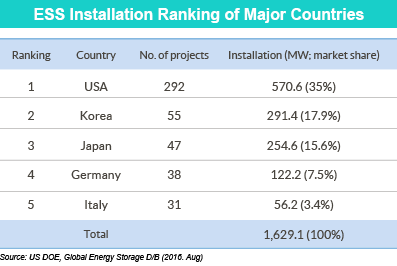
As of 2016, Korea's ESS installation level increased by 52.4 MWh and reached 291.4 MWh, or 18 percent of the world mar- ket share. Its share is slightly over half of the United States’ market share. Considering that Korea’s land mass is only about 1 percent of that of the United States, the volume of Korea's ESS installation is huge. Even other developed countries such as Japan, Germany and Italy are far behind Korea. Korea's lithium ion battery production is one of the world’s highest and contin- ues to increase rapidly. In particular, major Korean companies like LG Chem Ltd.
produces 591 MWh, while Samsung SDI’s
production level is 544 MWh, which is larger than those of oth-
er global major companies like China’s BYD (188 MWh) and
the U.S.’ Tesla (186 MWh). The domestic ESS market
increased to USD 263.1 million in 2016 and the country’s ESS
export also grew rapidly to USD 400 million last year.
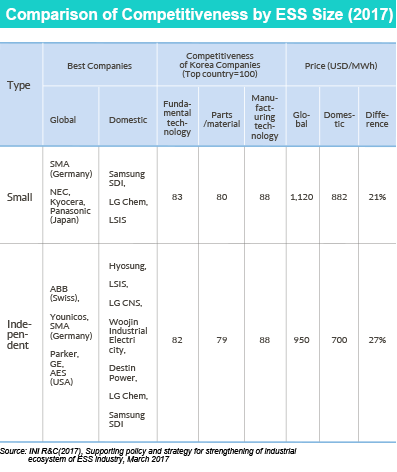
Korea’s ESS industry takes up a big share in the global mar- ket, but its overall competitiveness is relatively lower than major global companies. In the area of fundamental technology, Korea’s competitiveness level is about 82 to 83 percent of that of the world’s best. Its parts and material competitiveness stands at about 80 percent. But its manufacturing technology is higher, standing at approximately 88 percent. Korea’s ESS industry also boasts strong price competitiveness. The prices of the country’s ESS products are generally 21 to 27 percent lower than those of other global companies.
Major ESS companies in Korea are active players in the glob- al market. LG Chem and Samsung SDI are front runners. Hanhwa Q Cells and LSIS have developed a new business mod- el that combines photovoltaic and energy management systems. For the successful realization of this project, they are pursuing cooperation with KEPCO, a major electricity supplier in Korea. PCS is a crucial part of ESS installation. PCS can be thought of as a system that receives electricity from a power generating source within the ESS, and converts the form of electric energy for battery storage or sends it to another system. Experts esti- mate PCS' share makes up about 25 percent of the value of ESS. Destin Power is the strongest company in this field, while Kokam is chosen as the highest ranked global company by Bloomberg and Navigant Research.
The Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy (MOTIE) has introduced many efficient support measures to boost Korea’s ESS industry. These include the mandatory installation of ESS in public buildings and the revision of special ESS price reduc- tion. For public buildings, there are mandatory measures enforc- ing a minimum of 5 percent ESS installation for electricity con- tracts over 1 MW. Experts forecast that an additional market worth KRW 200 billion (USD 176.2 million) and 244 MWh of power will be created in 2020 if ESS is introduced to existing buildings.