- Home
- Investment Opportunities
- Latest Information
- Industry Focus
Industry Focus
- ICT
With universal access to ICT resources and technological capabilities, S. Korea, which adopted the world’s first commercial Code-Division Multiple Access (CDMA) network (IS-95A) in 1996, LTE-A and high-speed 4G LTE broadband services in 2013, and more recently the first nationwide 5G wireless network, has long been at the forefront of the global ICT industry.
S. Korea, positioned as the world’s leading tech innovator, has been topping the list of overall mobile phone sales since 2011, showcasing the latest technologies such as 5G-enabled phones or foldable gadgets in the premium smart phone segment.
Thanks to recent supply deals struck by some of the leading tech companies like Samsung Electronics with the U.S. mobile carriers to help stretch the reach of 5G, Korea has started to show substantial progress in the fields of networking hardware as well. Given that the prevalence of 5G services is predicted to be increasingly common throughout the world, such achievement appears to help boost its market presence in the coming years. Dubbed as a 5G pioneer, S. Korea was first in the world to launch commercial 5G service and has since been extending nationwide coverage of it, providing the best and the fastest internet connection in the global telecommunications sector.
▶ A Key Industry Driving Korea’s Economy
The ICT industry has been a growth driver of the economy, taking up nearly 9 percent of Korea’s gross domestic product (GDP) since 2011. In 2019, the industry’s real contribution to GDP reached 10.8 percent, equivalent to KRW 199 trillion.
The two main subsectors of the telecommunications industry, telecom equipment and services, are taking an agile approach to shifting market demand and technological trends, making constant investment in innovation, by which the ICT industry can gain growth momentum.
Sales figures of telecom equipment sold in the first six months of the year 2020 was KRW 19.5 trillion, up 5 percent year-over-year. The growth pattern was also observed in other segments as well: devices at 6 percent, networking hardware at 6 percent (KRW 0.1 trn) and wireless telecom services at 9 percent (KRW 1 trn) over the same period.
The overall performance reflects the bright outlook for the market as the launch of 5G commercial services has turned the industry sales positive since 2020 and soaring demand for subsequent generations of network technology such as exponential growth in mobile data traffic, which is closely associated with improved device and connection capabilities, the convergence between media and telecom services and greater access to cloud computing platforms is likely to further spur industry growth.
▶ 5G+ Strategy and the Digital New Deal: Master Plan for Post COVID-19 Digital Transformation
After its 5G debut, S. Korea rolled out a nationwide strategy, dubbed “5G Plus (5G+)” in April 2019, which entails business support policies to focus primarily on 10 5G-based industries (VR, AR, wearable devices, etc.) and five services (smart factory, immersive content, etc.) which are pivotal to the economy. Under this plan, Seoul will set a goal to represent 15 percent of the global market share by the end of 2026, adding 600,000 new jobs. To this end, it will promote private-public partnership to invest upwards of KRW 30 trillion into the formation of the world’s best 5G ecosystem and its nationwide coverage by 2022.
In addition, S. Korea will lead public sector financing, through which the authorities will launch business feasibility assessments and profitability analysis to substantiate the viability of the aforementioned five main services until 2021. Then, they push forward a follow-up measure called “5G Plus (5G+) Innovation,” designed to provide ubiquitous access to the new services from 2021 to 2025.
<10 Core Industries and 5 Core Services of the 5G+ Strategy>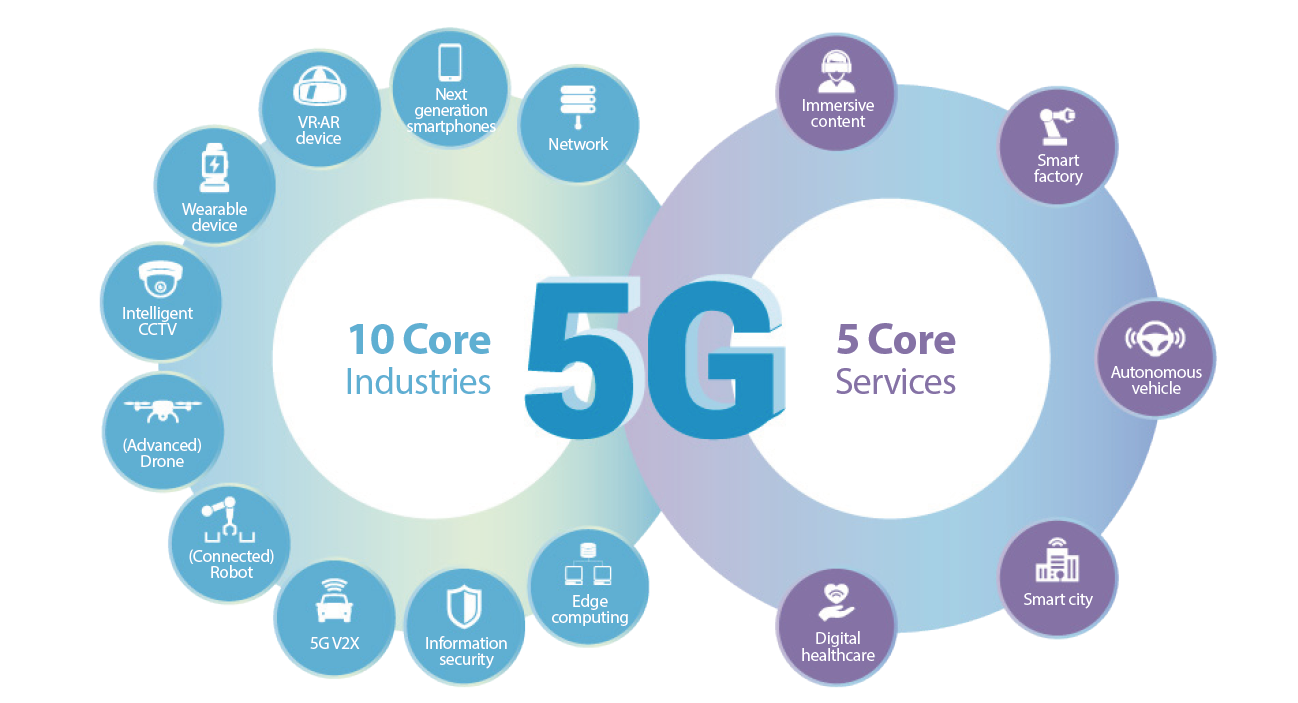
* * Source: 5G+ Strategy for Innovative Growth, Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT)
In accordance with the 5G + policies, the Korean government has formed a 5G+ strategy committee made up of both private and public entities who will take on the role of agenda setting for cross-government, private-public and multi-stakeholder partnerships.
Aside from the 5G+ initiative, the Moon administration proposed the Korean New Deal on July 2020, which is centered on two main pillars—the Green New Deal and the Digital New Deal. In combination with environmental schemes, the Digital New Deal would lay out a grand plan for the digital economy.
To carry out the policies, the S. Korean government plans to put greater emphasis on the development of a digital ecosystem underpinned by D.N.A. (an acronym standing for data, network and artificial intelligence) technologies in an effort to bolster the development of the productivity and production of digital goods and services. In addition, they have set the goal of cross sector convergence, making 5G, AI and data analytics technologies applicable to almost all industrial sectors, alongside digital inclusiveness which expands 5G coverage nationwide and cloud-based smart e-governance solutions harnessing 5G networks.
<5G Policies of the Digital New Deal>
| Policy | Objective | Budget(KRW 1trn) | Jobs(unit: 10,000) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ´20 ~´22 | ´20 ~´25 | ´20~´25 | ||
| Data Dam | ⦁Enhance data usability through collection, linkage and utilization of information from different sources
⦁Lead the world 5G and AI convergence | 8.5 | 18.1 | 38.9 |
| Smart Governance | ⦁Adopt digital application to make paperless e-governance
and smart workplace - (Smart workplace) 5G services available in government buildings/ Transfer public datasets to cloud platforms | 2.5 | 9.7 | 9.1 |
| Smart
Healthcare Infrastructure | ⦁Build smart medical infrastructure which lays foundations
for contact free remote healthcare service - (Smart health clinics) Formation of tech-based digital healthcare facilities | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.2 |
* Source: Korean New Deal Policy (※The budget and employment target on the table is based upon data sources on overall policy information.)
In an attempt to unlock the opportunities brought by superfast wireless services, global tech giants who have entered Korea are now joining the global race toward 5G. Swedish telecommunications company Ericsson, which has been a leader in mobile networking services since it first arrived and started to deploy 2G in Korea, recently partnered with a Korean carrier to co-invest in 5G research and development.
Taking from its years of experience in Korea, Finnish telecom equipment maker Nokia, has worked on advancing its overseas service quality and performance, while offering virtualized network services (VNS) and next generation network solutions which go beyond 5G.
Furthermore, a wide array of global tech companies in different subsectors of 5G, AI, cloud services, e-commerce applications, O2O (online to offline) platforms and even the game business, are coming to Korea in hopes of finding new growth opportunities. As such, the investment boom in Industry 4.0 technologies is projected to continue on for some time.
By Gil-Hyun Ahn (ghahn@gokea.org), Korea Electronics Association
< The opinions expressed in this article are the author’s own and do not reflect the views of KOTRA.>










