- Home
- Investment Opportunities
- Latest Information
- Industry Focus
Industry Focus
- ICT

Current Status of Korea's ICT Industry
Devices: Heightening Competition and Entry into New Industries
At the same time, major Korean players such as Samsung Electronics and LG Electronics are launching various electronic devices such as smart rings and smart lighting and expanding new industries in line with the spread of 5G networks, the popularity of smart homes, and the development of augmented and virtual reality technologies. They are responding to the digital transformation trend by maintaining their competitive advantage in premium smart phones and promoting new industries driven by key digital technologies.
Telecommunications: 5G Upgrade and 6G
As the development of convergence services is essential for the expansion of the 5G industry, the government and private players are investing in advancing them. By spreading specialized 5G networks (hereinafter referred to as e-um 5G), efforts are being made to boost convergence services using telecommunications such as autonomous driving, Internet of Things (IoT), smart factories, and AR/VR. On the other hand, Korea is relatively less competitive in the telecommunications equipment sector, and the growth of parts and equipment makers other than Samsung Electronics is needed. With the world’s major markets for 5G telecommunications equipment such as the U.S., Europe, and India becoming less dependent on China, competitive Korea telecommunications equipment companies are expected to seek further opportunities in overseas markets.
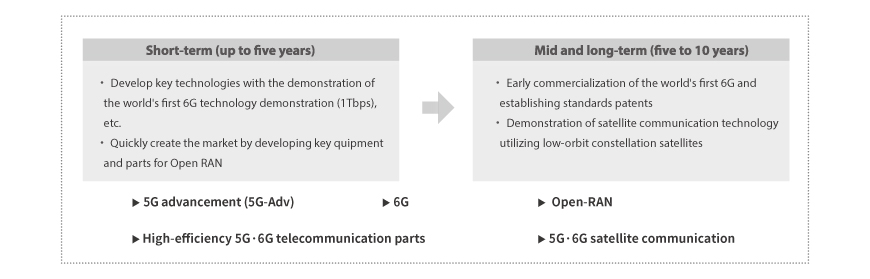
The global race for 6G has already begun, the next step after 5G with dramatically improved speed and latency. Korea is striving to lead the 6G era by working to demonstrate pre-6G technology (2026) and an integrated system (2030). As the 6G environment is expected to enable innovative services such as ultra-precise digital twins and UAM, Korea needs to secure its leadership in basic technologies and expand its presence in service areas.

Government Policies to Foster the ICT Industry
| ‘2020 5G+ Strategy Implementation Plan (‘Dec. 2019) | ‘2021 5G+ Strategy Implementation Plan (‘Jan. 2021) | ‘ 5G+ Convergence Services Promotion Strategy (‘Aug. 2021) | ‘2022 5G+ Strategy Implementation Plan(‘Feb. 2022) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Follow-up measures supporting each strategic 5G+ industry, etc. | Decision to introduce specialized networks, designation of a dedicated 5G+ agency, etc. | Identification of services for tackling social problems, development of domestic 5G modules and terminals, etc. | Advancement of 5G+ convergence services, spread e-um 5G services, etc. |
| Leading innovation | ‣ Description: Technology groups that are the backbone of the Korean economy and industry with significant ripple effects to upstream and downstream industries ‣ Technologies: Semiconductor, display, secondary battery, advanced mobility, next-generation nuclear energy ‣ Goal: Private-led development of super-gap technologies and reducing dependence on core material components |
|---|---|
| Challenging the future | ‣ Category: Technology groups showing rapid growth and having key interests from a national security perspective ‣ Technologies: High-tech bio, aerospace and offshore engineering, hydrogen, cybersecurity ‣ Goal: Scale up the market through private partnership and secure irreplaceable source technologies |
| Essential basic | ‣ Description: Common key and essential technology group needed across technologies and industries according to system transition ‣ Technologies: Artificial intelligence, next-generation communication, high-tech robot manufacturing and quantum ‣ Objective: Focus the capabilities of public and private sectors on public-led advancement of key source technologies and convergence and utilization of other strategic fields |
Next-generation Telecommunication: Detailed Objectives
By Gilhyun Ahn ( (ghahn@gokea.org))
Korea Electronics Association (KEA)
2)Korea’s 5G penetration status (Korea Eximbank, December 2022): (World’s No. 1) 415 5G base stations per 100,000 people and 52.2% of the population subscribed to 5G.
3)National Strategic Technology Development Plan: A plan established by the Korean government to develop future growth engines and ensure economic security by taking the global leadership in digital technology. Presents twelve national strategic technologies, fifty detailed priority technologies, and directions for their development in the short-, medium-, and long-term.
< The opinions expressed in this article are the author’s own and do not reflect the views of KOTRA>










