- Home
- Investment Opportunities
- Industries
- Renewable Energy
Renewable Energy
-
Facilitation of Energy Supply through Catch-up Technological Innovation CloseFacilitation of Energy Supply through Catch-up Technological InnovationCompetitiveness of Korea's technologyAccording to the World Energy Outlook 2022 released by the International Energy Agency (IEA), Korea is evaluated as a major player in the global solar industry value chain in terms of technology and production capacity (cell and module manufacturing)."Clean technologies"※ Source : World Energy Outlook 2022 (FIG 4.18), IEAAccording to the Korea Institute of Science and Technology Evaluation (KISTEP, 2021), Korea's technology level in the energy and resource sector in 2020 was 80.2% compared to the country with the highest level of technology (the United States), with a technology gap of 3.7 years.More specifically, Korea's photovoltaic (PV) technology within the new and renewable energy sector is evaluated to be 90.0% in the high-efficiency solar cell category, and Korean cell and module manufacturers (Hanwha Solutions, Hyundai Energy Solutions, etc.) based on their technology and the domestic market are entering overseas markets by building overseas factories.Moreover, Korea's wind power technology is 75.0% that of the US, and structural material manufacturers (Unison, CS Wind, etc.) are evaluated to be competitive in building towers and substructures. The industry plans to participate in the domestic market by building large-scale wind farms and strengthen global competitiveness by expanding investment.The hydrogen industry is building infrastructure to tap into hydrogen such as hydrogen cars and fuel cells, while adding infrastructure for green hydrogen production.
Korea's technology level in the energy and resource sector in 2020 Level of technology Energy source, Level of technology(%), Technology gap(years), Research capacity Energy source Level of technology(%) Technology gap(years) Research capacity 2018 2020 2018 2020 2018 2020 1. High-efficiency solar cell 87.5 90.0 2.0 1.0 Excellent Excellent 2. Wind power generation 74.0 75.0 5.0 5.0 Average Average 3. Bio and waste-to-energy 71.5 78.0 4.8 4.0 Excellent Excellent 4. Geothermal energy 68.5 69.0 5.0 5.0 Average Average 5. Marine energy 81.5 81.0 4.3 4.5 Excellent Excellent 6. Hydrogen and fuel cell 78.3 75.0 3.0 3.0 Excellent Excellent ※ Source : 2020 Technology Level Evaluation (KISTEP, April 2021) -
Korea’s New and Renewable Energy, an Emerging Market OpenKorea’s New and Renewable Energy, an Emerging MarketCurrent Status of Renewable Energy SupplyAccording to the Korea Energy Agency (KEA), new and renewable energy accounted for 8.29% of total power generation in 2021, an increase of 11.4% compared to the previous year. The cumulative installed capacity of new and renewable energy in 2021 was 30.2 GW, up 16.3% compared to the previous year. Solar power accounts for 70.2% and wind power accounts for 5.7% of total facilities (cumulative)."New and Renewable Energy: Installed Capacity and Power Generation"
New and Renewable Energy: Installed Capacity and Power Generation Category, Installed capacity (cumulative), Power generation Category Installed capacity (cumulative) Power generation 2019 2020 2021 2019 2020 2021 New and renewable energy 20,632 25,974 30,212 34,247,264 43,123,776 50,657,393 Renewable energy 19,813 25,013 29,072 30,909,337 37,202,048 43,668,518 Solar 12,745 17,357 21,199 14,192,911 19,337,964 24,717,623 Wind 1,494 1,645 1,709 2,679,248 3,149,948 3,180,017 Hydro 1,809 1,807 1,821 2,791,076 3,879,383 3,057,210 Marine 256 256 256 474,321 457,263 454,980 Bio 3,141 3,526 3,579 10,415,632 9,938,354 11,788,068 Waste 368 422 507 356,149 439,137 470,620 New energy 819 961 1,140 3,337,926 5,921,728 6,988,875 Fuel cell 473 615 794 2,306,654 3,544,354 4,798,120 IGCC 346 346 346 1,031,272 2,377,374 2,190,755 ※ Source: 2021 New and Renewable Energy Distribution Statistics (Korea Energy Agency, December 2022)
※ Includes renewable energy (solar, wind, hydro, bio, renewable waste, and marine energy) and new energy (fuel cell, hydro, and IGCC). Non-renewable waste is excluded according to the amendment to the Act on New and Renewable Energy (on October 2019).Current Status of the New and Renewable Energy IndustryAccording to the Korea Energy Agency (KEA), the sales volume of the new and renewable energy industry in 2021 amounted to about KRW 29 trillion, an increase of 13.6% year-on-year. Korea's new and renewable energy industry continues to grow: the number of companies in related areas such as renewable energy product manufacturing, construction, power generation, and services was 110,000, up 31.7% year-on-year, and the number of employees reached about 140,000, an increase of 19.4% year-on-year.Current Status of the New and Renewable Energy Industry Category, Number of Companies, Number of Employees, Sales (KRW 100 million) Category Number of Companies Number of Employees Sales (KRW 100 million) ’20 ’21 ’20 ’21 ’20 ’21 Manufacturing 499 536 12,353 11,864 107,369 121,191 Construction 2,169 2,144 17,617 14,937 71,886 64,544 Power generation and heat supply 78,276 104,132 82,810 108,462 62,696 87,352 Service 963 1,021 5,318 5,690 11,732 15,001 Total 81,907 107,833 118,098 140,953 253,683 288,087 ※ Source : 2021 New and Renewable Energy Industry Statistics (Korea Energy Agency, December 2022) -
Global Renewable Energy Companies Continue to Enter Korea OpenGlobal Renewable Energy Companies Continue to Enter Korea

Global Companies Located in Korea Country, Name of Company, Description Country Name of Company Description Denmark Vetas Invested approximately USD 300 million, including the establishment of a turbine parts production plant and the relocation of its Asia-Pacific regional headquarters to Korea (January 2023)
- (Expected effect) Vestas' investment is expected to make Korea a wind power manufacturing hub in the Asia-Pacific region, producing core parts for wind turbines and driving exports.China Jinko Solar Jinko Solar (module manufacturer) and TopInfra (Korean contractor) jointly supply N-type modules to an 8.5 MW-class project in Korea (March 2023) US GE Renewable Energy Signed a partnership with Hyundai Electric (Korea) for leveraging GE's offshore wind turbine technology in building production and supply network in Korea (December 2022)
- (Expected effects) Domestic production of key components of GE Renewable Energy's mega-sized wind turbines (i.e., nacelles and generators) and localization of various equipment and parts for the creation of supply network in Korea.UK Offsore Design Engineering Selected as the consulting company providing services related to preparation for a 384 MW-class offshore wind farm in Tongyeong, from basic design to EPC and supply of offshore wind turbines (May 2022) Denmark CIP CIP plans to partner with Korean companies for substructures, cables and engineering in the development and construction of offshore wind farms in Ulsan and Jeollanam-do (KRW 158 billion invested + KRW 310 billion planned, as of December 2022) 
-
Meeting Korea's Nationally Determined Contribution through Carbon-Neutrality and Green Growth CloseMeeting Korea's Nationally Determined Contribution through Carbon-Neutrality and Green GrowthCarbon Neutrality PlanThe government recently announced the 1st Master Plan for Carbon Neutrality and Green Growth (2023-2042) and announced a detailed plan to achieve the national greenhouse gas reduction targets by 2030. The master plan is Korea's first top-level plan for achieving carbon neutrality and green growth, established according to the Act on Carbon Neutrality and Green Growth enacted in March 2022. The government prepared a rational plan by considering the nation's economic and social conditions and feasibility of fulfilling greenhouse gas reduction targets.
 1st Master Plan for Carbon Neutrality and Green Growth (announced by the government in March 2023)
1st Master Plan for Carbon Neutrality and Green Growth (announced by the government in March 2023)- Defined the nation's power generation and 2030 GHG reduction targets for transition to a carbon-neutral society by 2050, and proposed policies for reduction and strengthening of foundation for implementation.
- Designated sector-specific reduction targets for meeting the 2030 National GHG
Reduction Targets (40% reduction from 2018 levels) and defined annual targets for the
first time.
- Especially noteworthy is the increased share of renewable energy generation in the transition category (7.5% in 2021 → above 21.6% by 2030)
 Plans for expanding energy and renewable energy sectorsRecent government policies to promote new and renewable energy are as follows
Plans for expanding energy and renewable energy sectorsRecent government policies to promote new and renewable energy are as follows
New government's energy policy directions (July 2022) ▲ Renewable energy policy improvement plan (November 2022) ▲ 10th Master Plan for Electricity Supply (January 2023)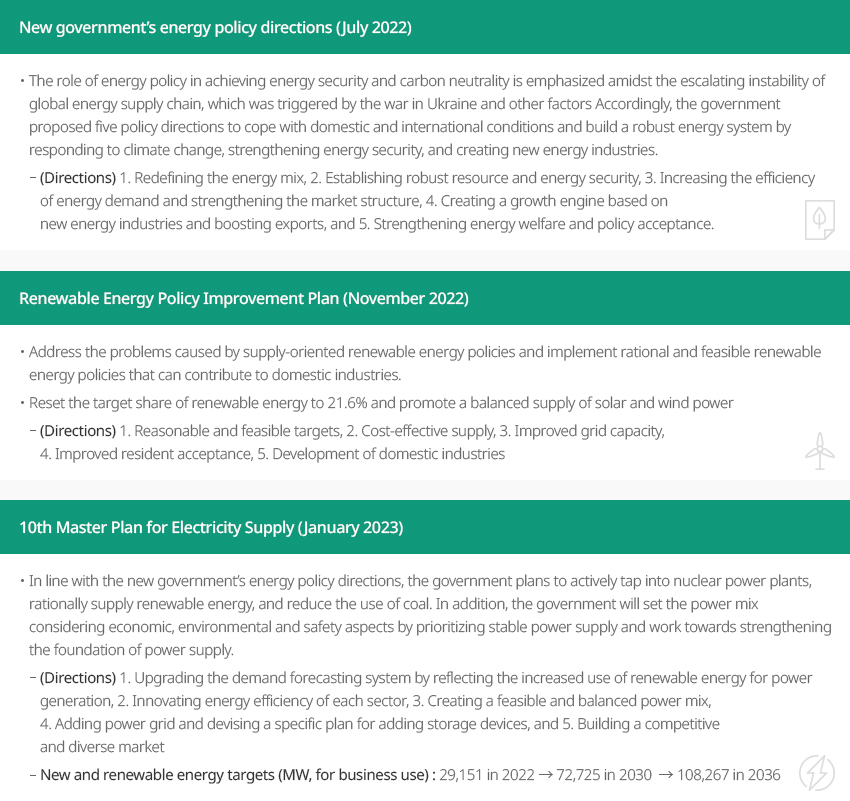 New government’s energy policy directions (July 2022)
New government’s energy policy directions (July 2022)- The role of energy policy in achieving energy security and carbon neutrality is
emphasized amidst the escalating instability of global energy supply chain, which was
triggered by the war in Ukraine and other factors Accordingly, the government proposed
five policy directions to cope with domestic and international conditions and build a
robust energy system by responding to climate change, strengthening energy security,
and creating new energy industries.
- (Directions) 1. Redefining the energy mix, 2. Establishing robust resource and energy security, 3. Increasing the efficiency of energy demand and strengthening the market structure, 4. Creating a growth engine based on new energy industries and boosting exports, and 5. Strengthening energy welfare and policy acceptance.
Renewable Energy Policy Improvement Plan (November 2022)- Address the problems caused by supply-oriented renewable energy policies and implement rational and feasible renewable energy policies that can contribute to domestic industries.
- Reset the target share of renewable energy to 21.6% and promote a balanced supply of
solar and wind power
- (Directions) 1. Reasonable and feasible targets, 2. Cost-effective supply, 3. Improved grid capacity, 4. Improved resident acceptance, 5. Development of domestic industries
10th Master Plan for Electricity Supply (January 2023)- In line with the new government’s energy policy directions, the government plans to
actively tap into nuclear power plants, rationally supply renewable energy, and reduce
the use of coal. In addition, the government will set the power mix considering
economic, environmental and safety aspects by prioritizing stable power supply and
work towards strengthening the foundation of power supply.
- (Directions) 1. Upgrading the demand forecasting system by reflecting the increased use of renewable energy for power generation, 2. Innovating energy efficiency of each sector, 3. Creating a feasible and balanced power mix, 4. Adding power grid and devising a specific plan for adding storage devices, and 5. Building a competitive and diverse market
- New and renewable energy targets (MW, for business use): 29,151 in 2022 → 72,725 in 2030 → 108,267 in 2036

-
Establishment of Industrial Ecosystem Differentiated by Region OpenEstablishment of Industrial Ecosystem Differentiated by RegionRegions with a new and renewable energy industry base or planned large-scale projects are working to strengthen the foundation for building an industrial ecosystem that is differentiated for each region. Local governments will play a leading role in discovering and promoting customized, large-scale projects for their regions, and the central government will support the establishment of infrastructure, R&D demonstration, and human resource development.
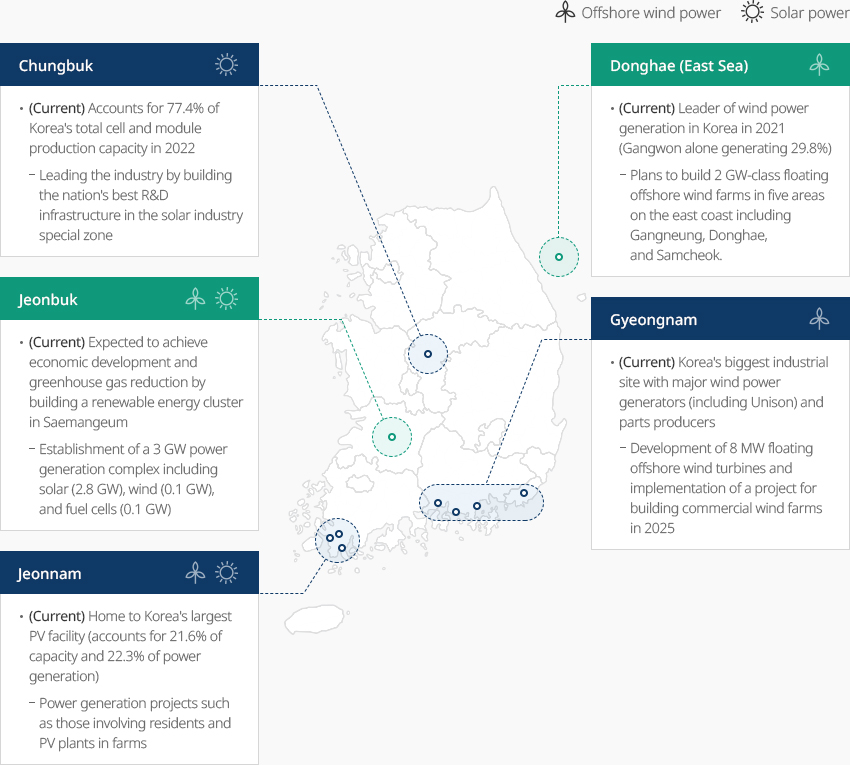
- Chungbuk(Solar power)
- (Current) Accounts for 77.4% of Korea's total cell and module production capacity in 2022 - Leading the industry by building the nation's best R&D infrastructure in the solar industry special zone
- Donghae (East Sea)(Offshore wind power)
- (Current) Leader of wind power generation in Korea in 2021 (Gangwon alone generating 29.8%) - Plans to build 2 GW-class floating offshore wind farms in five areas on the east coast including Gangneung, Donghae, and Samcheok.
- Jeonbuk(Solar power, Offshore wind power)
- (Current) Expected to achieve economic development and greenhouse gas reduction by building a renewable energy cluster in Saemangeum - Establishment of a 3 GW power generation complex including solar (2.8 GW), wind (0.1 GW), and fuel cells (0.1 GW)
- Gyeongnam(Offshore wind power)
- (Current) Korea's biggest industrial site with major wind power generators (including Unison) and parts producers - Development of 8 MW floating offshore wind turbines and implementation of a project for building commercial wind farms in 2025
- Jeonnam(Solar power, Offshore wind power)
- (Current) Home to Korea's largest PV facility (accounts for 21.6% of capacity and 22.3% of power generation) - Power generation projects such as those involving residents and PV plants in farms
 ※ Source : Korea Energy Agency (KEA)
※ Source : Korea Energy Agency (KEA) - Chungbuk(Solar power)
-
Complex nameBit-Green Industrial Complex
-
Initial designation date2009.09.30
-
Designated area(m2)4,070,692
-
ManagementKorea Industrial Complex Corporation
-
Nearby RailwayHampyeong Station
-
Distance from station(km)30
-
Nearby AirportGwangju Airport
-
Distance from airport(km)20
-
Industrial water Supply capacity(ton/day)17130(㎥/day)
-
Affiliation local governmentGwangju Metropolitan City Gwangsan-gu, Jeollanam-do Hampyeong County
-
Population1,454,154
-
Complex nameSaemangeum District National Industrial Complex
-
Initial designation date2019.08.02
-
Designated area(m2)18,495,346
-
ManagementSaemangeum Development Agency
-
Nearby RailwayGunsan Station
-
Distance from station(km)28
-
Nearby AirportGunsan Airport
-
Distance from airport(km)15
-
Industrial water Supply capacity(ton/day)123077(㎥/day)
-
Affiliation local governmentJeollabuk-do Gunsan City
-
Population267,982
-
Complex nameUlsan Techno General Industrial Complex(Ulsan Free Economic Zone)
-
Initial designation date2013.06.20
-
Designated area(m2)1,286,977
-
ManagementUlsan Metropolitan City
-
Nearby RailwayTaehwagang Station
-
Distance from station(km)9
-
Nearby AirportUlsan Airport
-
Distance from airport(km)15
-
Industrial water Supply capacity(ton/day)2614(㎥/day)
-
Affiliation local governmentUlsan Metropolitan City Nam-gu
-
Population1,140,310
-
Complex nameChunhwa Agricultural Industrial Complex
-
Initial designation date2008.07.02
-
Designated area(m2)211,785
-
ManagementGyeongsangnam-do Miryang City
-
Nearby RailwaySangdong Station
-
Distance from station(km)14
-
Nearby AirportGimhae International Airport
-
Distance from airport(km)56
-
Industrial water Supply capacity(ton/day)633(㎥/day)
-
Affiliation local governmentGyeongsangnam-do Miryang City
-
Population105,099
-
Complex nameNamdong National Industrial Complex (Renewable Business District)
-
Initial designation date1980.09.02
-
Designated area(m2)9,504,046
-
ManagementKorea Industrial Complex Corporation
-
Nearby RailwayBupyeong Station
-
Distance from station(km)9
-
Nearby AirportIncheon Airport
-
Distance from airport(km)32
-
Industrial water Supply capacity(ton/day)49081(㎥/day)
-
Affiliation local governmentIncheon Metropolitan City Namdong-gu
-
Population2,943,491
-
Complex nameHaso Eco-friendly General Industrial Complex
-
Initial designation date2012.05.11
-
Designated area(m2)306,703
-
ManagementDaejeon Metropolitan City
-
Nearby RailwayDaejeon Station
-
Distance from station(km)17
-
Nearby AirportCheongju International Airport
-
Distance from airport(km)71
-
Industrial water Supply capacity(ton/day)1300(㎥/day)
-
Affiliation local governmentDaejeon Metropolitan City Dong-gu
-
Population1,469,431












