- Home
- Investment Guide
- Investment Process
- Establishment of Legal Corporate Entities
- How Foreigners Can Start Business in Korea
How Foreigners Can Start Business in Korea
- How foreigners can start business in Korea
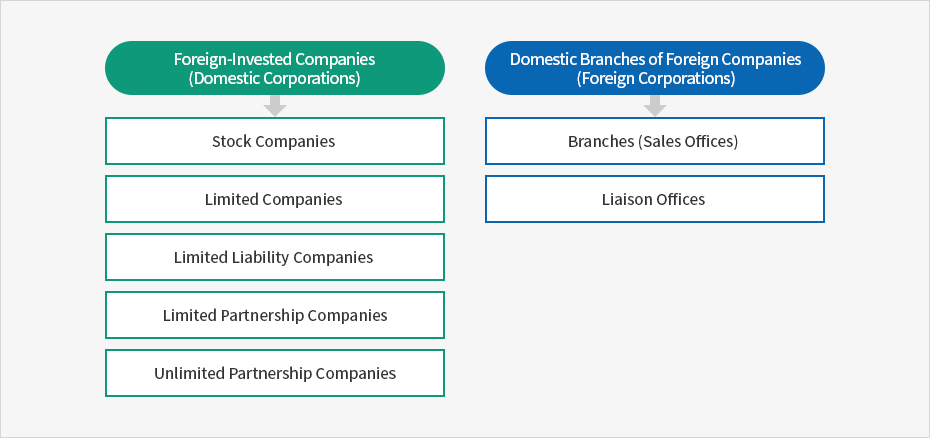
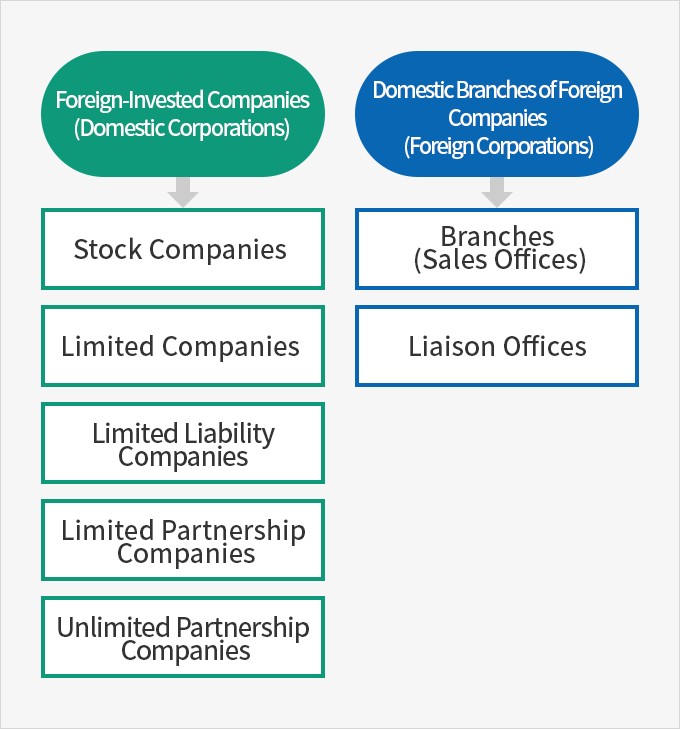
- Types of Foreign Enterprises(FIE)
- Incorporation Procedure
-
Foreign-Invested Companies (Domestic Corporations)
- Stock Companies
- Limited Companies
- Limited Liability Companies
- Limited Partnership Companies
- Unlimited Partnership Companies
-
Domestic Branches of Foreign Companies (Foreign Corporations)
- Branches (Sales Offices)
- Liaison Offices
Comparison of Foreign-Invested Companies, Domestic Branches of Foreign Companies, and Liaison Offices
| Category | Foreign-Invested Company | Domestic Branch | Liaison Office |
|---|---|---|---|
| Governing Law | Foreign Investment Promotion Act | Foreign Exchange Transaction Act | Foreign Exchange Transaction Act |
| Type of Corporation | Domestic | Foreign | Foreign |
| Recognized as FDI | Yes | No | No |
| Company Name | No restrictions | Identical to that of headquarters | Identical to that of headquarters |
| Scope of Business Activities | No restrictions, within the permitted scope | Same activities as headquarters; within the permitted scope | Profit-making activities not permitted; purpose of establishing business contacts only |
| Minimum Investment Amount | KRW 100 million1) | N/A | N/A |
| Legal Liability | Limited to domestic corporations | Extend to headquarters | Extend to headquarters |
| Independence | Legally independent | Subordinated to headquarters | Subordinated to headquarters |
| Domestic Loans | Possible depending on credit rating of the domestic corporation | Almost impossible | Impossible |
| Establishment Procedures |
1. Notify FDI 2. Remit investment funds 3. Register corporation 4. Register business license 5. Register foreign-invested company |
1. Notify domestic branch establishment 2. Register corporation 3. Register business license |
1. Notify domestic branch establishment 2. Register identification number |
| Accounting and Taxation | Must record and maintain bookkeeping according to Korean Accepted Accounting Principles; obligated to receive external audits on certain conditions | Must record and maintain bookkeeping according to Korean Accepted Accounting Principles; not obligated to receive external audits | Not obligated to record bookkeeping |
| Corporate Tax Rate | Liable to taxation | Liable to taxation | N/A |
| Taxable Income | All profit made by a domestic corporation | All profit including domestic source income made by a domestic corporation; branch tax applicable to some countries | N/A |
| Tax Benefits | Tax benefits for foreign-invested companies and SMEs according to the Restriction of Special Taxation Act | N/A | N/A |










