Hydrogen Industry
- Home
- Business Opportunities
- Hydrogen Industry
Classification of Hydrogen Production Methods and Environmental Impact
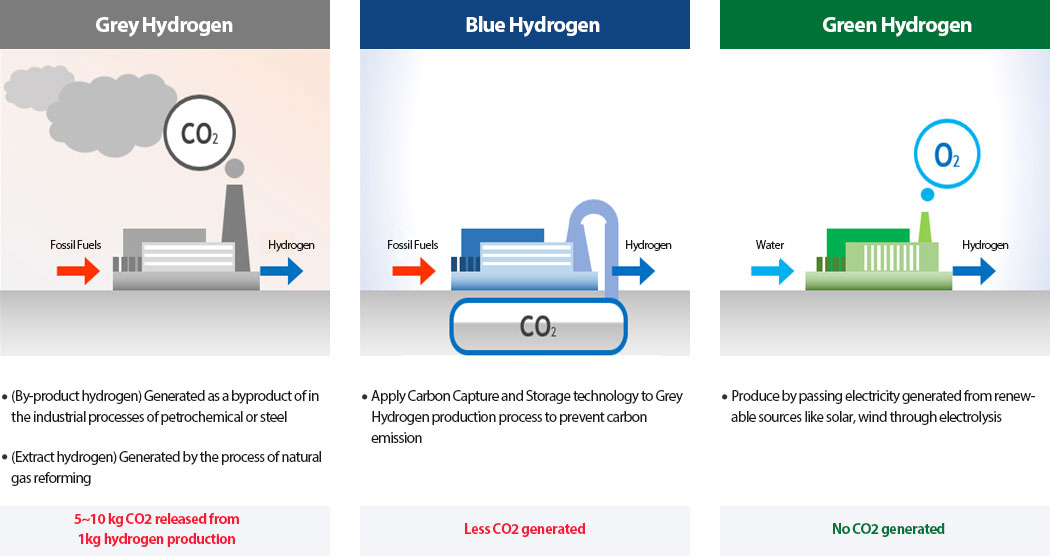
Gray Hydrogen
- Refers to by-product hydrogen produced during the naphtha cracking process in refining or hydrogen produced by reforming (extracting) natural gas.
- Producing 1 ton of gray hydrogen emits 10 tons of carbon dioxide.
Blue Hydrogen
- Hydrogen produced by capturing and storing the carbon dioxide emissions from gray hydrogen production, thereby reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Green Hydrogen
- Hydrogen produced by electrolysis of water using renewable energy, with zero greenhouse gas emissions.
What is the Hydrogen Ecosystem?
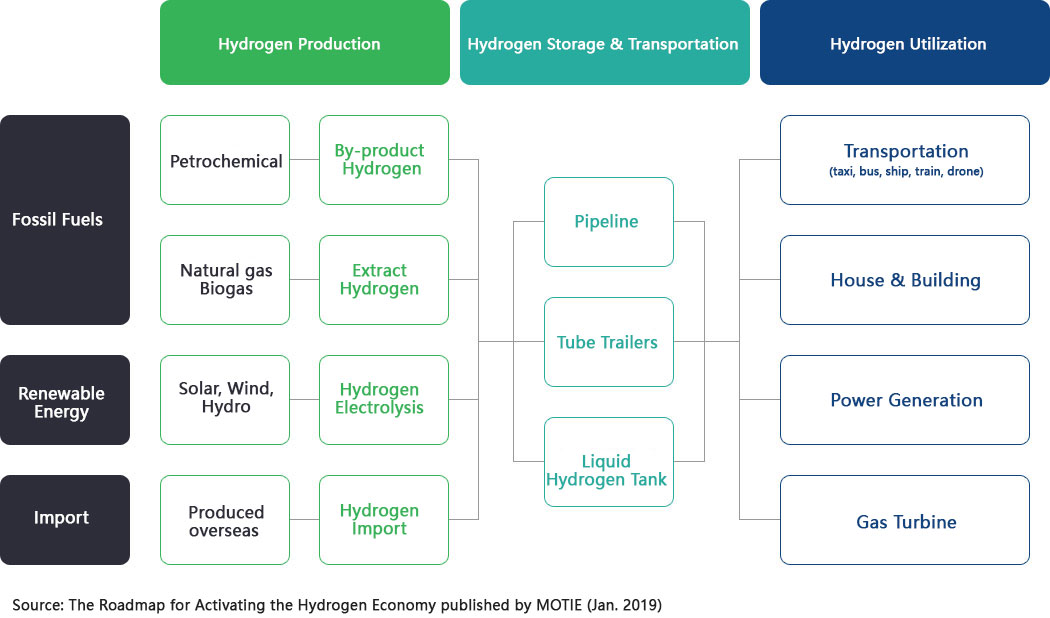
The hydrogen ecosystem consists of the production, storage, transportation, and utilization of hydrogen, and it is a complex system that links and interacts with various industries throughout the entire value chain.
Production
The stage where hydrogen is produced from other energy sources. It can be classified as "by-product hydrogen," "extracted hydrogen," or "electrolyzed hydrogen." Hydrogen can also be imported from overseas.
- By-product Hydrogen: Hydrogen that naturally occurs as a by-product in various industrial processes, mainly in petrochemical plants (oil refining) or steel mills (coke production)
- Extracted Hydrogen: Hydrogen that is extracted through chemical reactions, such as reforming natural gas or biogas. This is also referred to as "reformed hydrogen."
- Electrolyzed Hydrogen: Hydrogen produced by electrolyzing water using electricity from renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, or hydropower, which results in zero CO2 emissions and is often called "green hydrogen."
- Overseas Production: Hydrogen produced from overseas renewable energy or coal, often from hydrogen hubs or production sites abroad.
Storage and Transportation
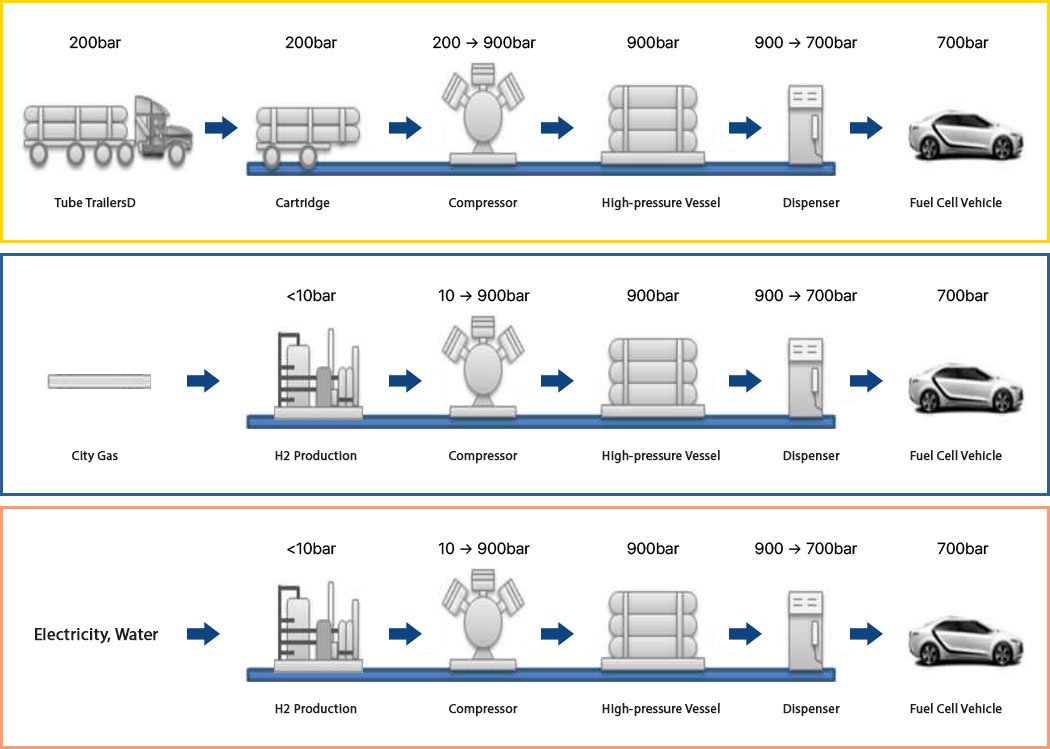
The stage where hydrogen is stored and transported from production sites to consumption areas, using methods such as "pipelines," "tube trailers," or "liquid tankers."
- Pipeline: Direct transportation of hydrogen through pipelines from production to consumption sites, using low-pressure gas hydrogen similar to city gas.
- Tube Trailer: A method of filling a cylinder-shaped tube container with compressed hydrogen gas at high pressure and bundling several of these together to secure them to a truck for transportation.
- Liquid Tanker: As liquid hydrogen can be transported in larger quantities than gas hydrogen, it is transported in liquid hydrogen containers via truck.
Utilization
The stage where hydrogen is used as energy, primarily in transportation, buildings, and power generation.
- Transportation: Mobility using hydrogen as fuel, such as hydrogen cars, hydrogen taxis/buses, hydrogen ships, hydrogen trains, and hydrogen drones
- Residential and Commercial Use: Small and medium-sized fuel cells are installed in homes and offices to provide heat and electricity
- Power Generation: Large-scale fuel cells are installed in power plants to supply heat and electricity to local areas
- Gas Turbines: Power generation gas turbines, which typically use natural gas, can be converted to run on hydrogen, supplying heat and electricity to local areas
Vision and Strategy
Vision
Jeonbuk State to Lead the 2050 Carbon Neutrality, Focused on Green Hydrogen Industry
Goal
-
No. 1 in green hydrogen production
100,000 tons per year, accounting for 10% of domestic hydrogen production (by 2030) -
Hydrogen convergence specialized industry
Carbon convergence hydrogen storage, a leading medium-large scale hydrogen mobility region -
Foundation for Hydrogen Society
Deployment of 20,000 hydrogen cars, 50 or more hydrogen charging stations
Strategy
| (Specialized) Establishing Green Hydrogen Hubs | (Convergence) Hydrogen Convergence with Jeonbuk’s Strategic Industries |
|---|---|
|
ㆍProduction of green hydrogen linked to renewable energy in Saemangeum. ㆍEstablishment of the infrastructure for utilizing green hydrogen. |
ㆍPromoting the convergence of large and medium-sized hydrogen mobility industries by linking Jeonbuk’s strategic industries, such as construction machinery, commercial vehicles, and agricultural machinery ㆍ Positioning Jeonbuk as a leader in the convergence of next-generation large and medium-sized hydrogen mobility industries. |
| (Deployment) Facilitate the utilization of hydrogen | (Environment) Systematic hydrogen security, and fostering of companies |
|
ㆍBuilding the hydrogen supply infrastructure, including hydrogen cars and charging stations. ㆍLeading the distribution of hydrogen fuel cells in rural and agricultural areas. |
ㆍEnsuring community acceptance of hydrogen and creating a hydrogen-friendly environment. ㆍEstablishing a systematic hydrogen industry development framework, including professional personnel and governance. |
Major Projects
- Hydrogen-Specialized National Industrial Complex (2023–2030, Wanju): Fostering mid-to-large hydrogen mobility and hydrogen storage containers, as well as creating an industrial cluster of related companies.
- Hydrogen City Development (Jeonju-Wanju 2020–2023 / Buan 2024–2027):
- Creating a city where hydrogen is used as an energy source in residential and transportation sectors - Hydrogen Product Testing and Certification Center (2021–2024, Wanju):
- Testing, evaluating, and certifying hydrogen products and facilities under the "Hydrogen Act." - Post-Use Fuel Cell Infrastructure (2021–2025, Wanju):
- Establishing certification and standards for the reuse and recycling of hydrogen fuel cells. - Polymer Fuel Cell Reliability Evaluation Center (2019–2024, Buan):
- Establishing a foundation for the evaluation and reliability improvement of polymer fuel cells - Electrolysis-Based Hydrogen Production Base (2022–2025, Buan):
- Building clean hydrogen production infrastructure with electrolysis, aiming for 1 ton/day of production capacity (2.5 MW) - Hydrogen Supply (Extraction) Base (2021–2024, Wanju)
- Creating a hydrogen supply base using natural gas reforming to produce 2.4 tons of hydrogen per day - Hydrogen Vehicle Fuel Cell Recycling Test and Certification Center (2024–2028, Wanju)
- Establishing a commercialization and testing center for the remanufacturing, reuse, and recycling of hydrogen vehicle fuel cells