Intellectual Property System
Intellectual property rights are classified into industrial property rights, copyrights, and new intellectual property rights. Industrial property rights consist of patent rights, utility model rights, design rights, and trademark rights. This text focuses on industrial property rights that are applied to general companies.
Patent Rights
The patent right system has been established to promote the development of the national industry by protecting and fostering inventions, and to this end, the system grants patent rights in return for the disclosure of technologies. The right is effective only within the countries which have obtained such a right. Korea adopts a first-to-file rule that grants patent rights to the first applicants.
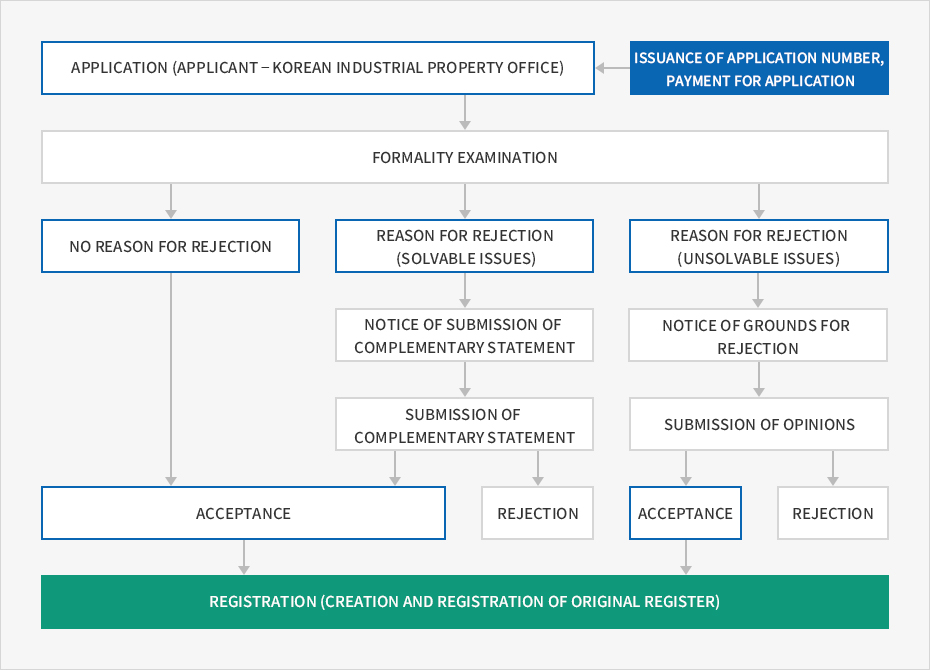
Main Procedures for Patent Application


- Formality Examination
- Disclosure of Application
- Substantive Examination
- Decision on Patent
- Publication of Registration

- A formality examination is conducted to check whether there are any defects in the process of filling in essential details in a form, compliance with deadline, attachment of certificates, payment of fees, etc.
- The disclosure of application refers to a system by which the Korean Intellectual Property Office discloses the details of the technology concerned to the public one and a half years after the application date to prevent delays in the examination and consequential disclosure of technologies for which an application has been submitted.
- A substantive examination is conducted to review the patent requirements of the technology such as industrial applicability, novelty, and inventiveness. As a patent is granted on condition of disclosure, the examination also focuses on whether the application is easily comprehensible to the public.
- A decision is made to grant a patent when the application meets certain patent requirements.
- Upon the decision to grant a patent, the applicant pays a registration fee to register the patent. From that point, the patent right enters into effect and the registered application for the patent will be published and disclosed to the public.
Method of Patent Application
Utility Model Rights
While patent rights protect inventions, utility model rights protect designs. Thus, utility model refers to the design itself which improves an existing invention to make it more convenient and useful. The registration system for utility model rights helps determine whether to register a utility model after conducting a substantive examination.
Design Rights
Design rights refer to the exclusive rights enjoyed by the registrant for all designs that create an aesthetic impression through visual aspects such as the form, shape or color of goods, or a combination of those factors. If the applicant wishes to apply for a design similar to the previously applied basic design, the design can be recognized as a related design upon the application within one year from the registration date of the basic design and thereby obtain the design right.
Trademark Rights
Trademark rights refer to the rights to exclusively use the labels that identify a particular product. Labels refer to all markings that are used to indicate the source of a product, regardless of its composition or manner of expression, including symbols, letters, shapes, sounds, smells, stereoscopic features, holograms, actions, or colors. Trademark rights last for ten years from the registration date and an application for renewal is required every ten years.