Main Services of the Korea Intellectual Property Office
With technological innovation and intellectual property policies at the core of the national strategy due to the Fourth Industrial Revolution, the Korean Intellectual Property Office is pursuing policies designed to foster related talent and improve public services in addition to providing reliable examination and judgement services, strengthening patent support and protection, and promoting the commercialization of superior intellectual properties.
Patent Examination System Customized in Three Tracks
The Korea Intellectual Property Office operates a patent examination system customized in three tracks to offer competitive services with regard to the examination period and quality: preferential examinations, general examinations, and late examinations. This system has several advantages in providing the opportunity to secure monopolistic status through the swift acquisition of patents, and securing sufficient time for commercialization through late examinations, which allows adjustment of the examination period when necessary.
- Preferential examinations : Request an investigation of a prior technology at a specialized institution and adjust the processing period for the application
- General examinations : Provide results within the average examination period
- Late examinations : Introduce an application system that allows delayed examinations upon customer request
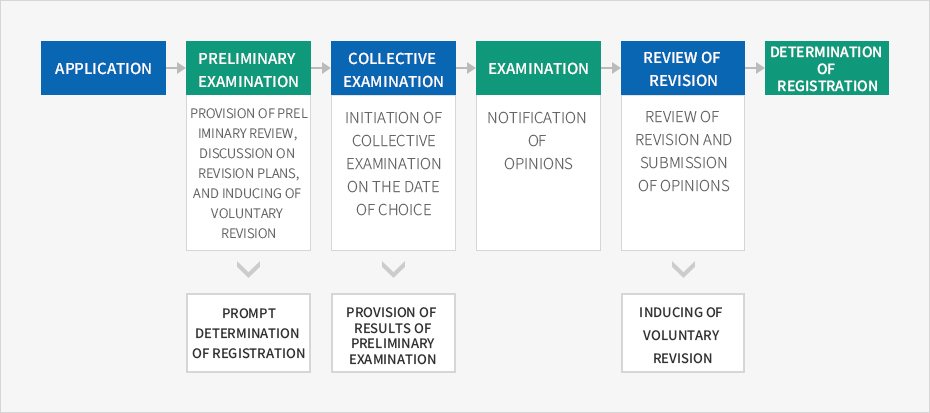
Preliminary Examinations
The patent applicant can identify and respond to any reasons for rejection before the official examination by exchanging opinions based on the results of the preliminary review by examiners, meanwhile examiners can review and grant patent rights in a more accurate and swift manner by exchanging opinions with the applicant regarding the concerned technology and examination itself.
Collective Examinations
Through reviews of multiple applications at one time at a time of their choosing, companies can secure collective intellectual property rights in line with new product releases, etc. in accordance with their business strategies, and the country as a whole can commercialize the outcome of R&D efforts and promote technology transfer.
Review of Revisions
Through this system, patent applicants exchange opinions on revisions through a consultation with examiners before submitting final amendments to their applications in cases of refusal notifications. By doing so, applicants can advance the timing of patent decisions by identifying chances for resolving refusals and thereby reducing unnecessary procedures, while examiners can ensure accurate examinations by exchanging opinions on the technologies and examinations with applicants.
Online Technology Publication Service
The Korea Intellectual Property Office has created a “Cyber Bulletin” to operate an online technology publication service through its website. In many cases, the existing application system forced holders of certain technologies, for which exercising patents was difficult, to apply for additional patents for the purposes of defense, resulting in wastes of time and cost. Thus, when those who have no intention to secure patent rights but still seek protection from the exercise of patent rights of others posts details of their technology on the Cyber Bulletin, the Korea Intellectual Property Office notarizes the contents and date of the technology concerned and recognizes the priority, thereby preventing any disadvantages in business from other companies’ exercising of patent rights.